The What, Why, When, and How of Storyboarding
An important concept for developers/designers!
As developers, we design products almost all the time. Understanding users' feelings is extremely important since the product is to be made for them. This can be achieved through storyboarding!
What is Storyboarding?
It is a UX tool that helps you to visually predict and explore a user's experience with a product. It is a linear sequence of illustrations that are arranged together to visualize a story. Storyboards help the designers to string together various personas, user stories, and various research findings to develop requirements for the product. The combo of images and words makes even the most complex ideas clear and easy to understand.
Why use Storyboards?
Storyboarding has a lot of benefits. I have listed only 4 of them here as examples to help you guys truly understand why storyboarding is so important!
1. A Human-Centered Approach
Storyboards make the design approach human-centered by putting people at the heart of the design process. They tend to put a human face on the research findings and analytics.
2. Forces thinking about user flow
With the help of storyboarding, the designers are able to walk in the shoes of their users. This makes them see the products in a similar light. Therefore, they are able to understand the existing scenarios of interaction. They are also able to test hypotheses about potential scenarios.
3. Prioritizing what’s important
If you are working at a startup, a small company or on your personal project, chances are that your budget is not big enough. Thanks to storyboards, you can cut out a lot of unnecessary work as they reveal what you don't need to spend unnecessary money on.
4. Simpler iteration
The concept of storyboarding depends on an iterative approach. Sketching has no cost at all. So, designers can experiment as much as they want and however they want. Even if you working with a team, you can shoot down ideas and present new innovative solutions and nobody would get mad. That's because no one gets attached to quick and rough ideas ;)
When to use storyboards?
Storyboards are extremely useful when you are participating in a "participatory design", design sprints, and hackathons. In "participatory design", the participants include stakeholders, UI and UX designers, developers, researchers in the design process. This "participatory design" concept is implemented to ensure that the end result is as good as possible. With a persuasive and compelling storyboard, the product is more likely to be "attractive" to the target audience. Communicating design decisions with a storyboard really comes in handy in a lot of various scenarios!
How to design a Storyboard?
You can easily create a storyboard by following these 5 steps:
1. Research
Real data forms the foundation of storyboarding. This data is obtained through UX research. To do so, read user interviews, perform field research, talk to an experienced product team, or compile a bunch of information from any reliable source in order to gain adequate knowledge about user stories.
2. Pick a flow to focus on
3. Write down the plot steps and basic outline of the story
Imagine the steps and events of the user story. Work on these basic parts of the user story:
- The main character
- Scene/environment
- Think through the places, the environment where the story takes place
- List of problems or solutions occurring throughout your story
4. Add emotions and scene details
Add emoticons or write the state of the user's emotions as he takes every step.
5. Create the storyboard!
Now is the time to make things happen! Grab any marker or pen and draw your story. You should create them on separate pages so you can make any changes if required.
Types of Storyboards
There are two types of Storyboards:
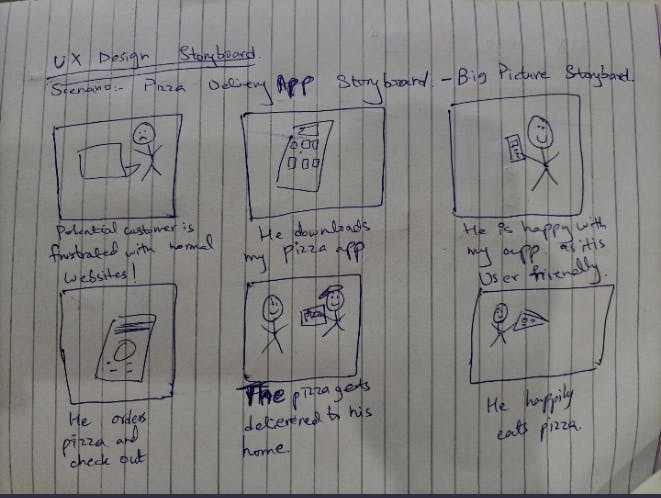
1. Big Picture Storyboards
It is much more focused on the "how" and "why" behind the user's engagement with the design. It depicts the emotional engagement a user will have with your product. It focuses on the user and the user's environment. Moreover, it focuses on the specific needs or pain points of the user.
Let's take a look at an example:
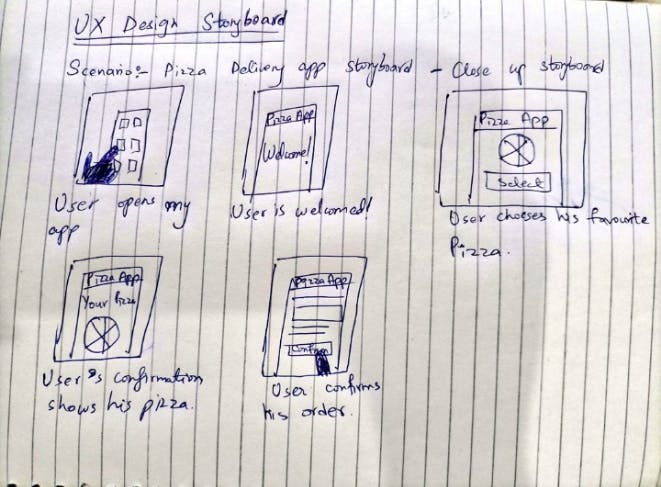
2. Close-up Storyboards
It focuses on the "what". For example:
What is happening on this screen?
What will the user do to transition between screens?
What are some potential problems with the product flow.
In simple words, it focuses on the product.
Let's take a look at an example:
Conclusion
That's all about storyboarding! If you are a CS or SE student, chances are that if you choose a project like a game as your Final Year Project, you'll have to create storyboards. Even as a Junior or Senior developer/designer, you might have to create a storyboard for your projects. Therefore, it is important that you are good at this.
Let's connect!
✨ Github